
Let’s build the future together.
Great ideas need great people. Partner with us to bring your vision to life, or take the first step in your career by joining our team of innovators.

Tim Berners-Lee, known as the ‘Father of the Web‘, discovered HTML in 1990 while working with his peers at the CERN lab. The need arose when they had to share research papers online with colleagues. It transformed simple word processor documents into viewable online files.
HTML, which is the basis of web page development, allows developers to shape content and develop websites. In this article, we will look into HTML’s advantages like browser compatibility, flexibility, speed, and ease of learning, as well as its disadvantages like weak security, code length, and complexity in creating complex layouts.
HTML (Hypertext Markup Language) is a standard markup language. Web developers depend on it to create the core structure of a webpage, including layout, text, and images, all of which we will look deeper into while exploring the advantages of HTML.
HTML furnishes an array of tags and elements that dictate how content is organized and displayed on a webpage. Developers use these tags and details to explain what content means, making it easy for people to understand.
As of 2022, JavaScript and HTML/CSS were the most commonly used programming languages among software developers around the world, with more than 63.6 percent of respondents stating that they used JavaScript and just around 53 percent using HTML/CSS. Python, SQL, and TypeScript rounded out the top five most widely used programming languages around the world.
Sign up with ellow, access 25,000+ pre-vetted developer profiles, and start building your development team in 48 hours.
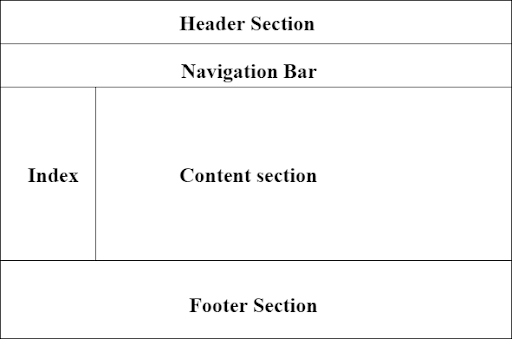
The basic structure of HTML has five main elements:
An HTML file’s DOCTYPE declaration comes right at the top. It tells web browsers which version of HTML is being used in the document. The declaration ensures proper display of the webpage.
HTML files are built using HTML tags, which are enclosed in angle brackets (< >). These HTML tags provide structure and meaning to the content. The opening tag indicates the beginning, while the closing tag indicates the end.
The <head> section is where you include information about the webpage, such as its title, character encoding, linked stylesheets, and more. This information is not directly displayed on the webpage but is essential for proper presentation and SEO.
The <body> section contains the visible content of the webpage that users see when they visit the site. This is where you include headings, paragraphs, images, links, and other interactive elements.
HTML elements can be nested within each other, creating a hierarchical structure. For instance, you can place a <p> (paragraph) element inside a <div> (division) element to organize content.
An Example of basic structure:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>My First Web Page</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Welcome to My Page</h1>
<p>This is a simple example of HTML. </p>
</body>
</html>
HTML enjoys widespread browser support, making it a universal language for web content. Web browsers like Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Internet Explorer obey HTML standards so that their web pages look the same on all different platforms.
As Tim Berners-Lee, the inventor of the World Wide Web, said, “HTML is the lingua franca for publishing on the Web.“
Lingua Franca: A language that is adopted as a common language between speakers whose native languages are different.
One of HTML’s important advantages is its cost-efficiency. Developers don’t need to purchase licenses or additional software to create HTML content.
This cost-effectiveness has led to HTML being the foundation of the web, as observed by Marc Andreessen, co-founder of Netscape: “HTML is precisely what we were trying to prevent—a rich programming environment for developing custom applications on top of a general-purpose computer.”
HTML is simple and easy to learn. It is so easy to learn that school students can use HTML to create their own basic website with images and colors.
Vincent Tan, a web developer, aptly puts it, “HTML is like building with Lego bricks; it’s easy to grasp and lets you create beautiful structures quickly.”
HTML’s loose syntax grants developers flexibility. It allows for creative experimentation and adapts to various content types. This versatility is crucial for crafting diverse web experiences.
Jeff Atwood, co-founder of Stack Overflow, noted, “HTML is the canvas of the web. It’s the foundation for the entire web experience.”
HTML’s lightweight nature ensures fast loading times for web pages By reducing the loading time, HTML saves time for users.
HTML extends its capabilities to data storage with technologies like XML. It enables the structured storage of data within web documents, making it retrievable and usable by applications. This data accessibility is vital in modern web development.
As Tim Bray, co-editor of the XML specification, said, “XML is a widely-used standard for representing structured data.”
It’s essential to understand these drawbacks to make informed decisions and explore alternative solutions where necessary.
HTML is a static language. It defines the structure and presentation of web content but cannot produce dynamic interactions by itself. As a result, creating interactive web applications, like online games or real-time chat systems, can be challenging with HTML alone. For dynamic functionalities, Web developers often turn to JavaScript, a scripting language that complements HTML’s static nature.
Developers often use JavaScript frameworks to develop dynamic web applications,
Creating and maintaining the structure of HTML documents is complex, mainly for large-scale projects. As webpages grow in complexity, managing nested HTML elements is challenging. This complexity may lead to errors.
Some web developers opt for more structured approaches using template engines like Handlebars or libraries like JSX (for React). These tools offer a cleaner way to organize HTML-like code within JavaScript.
HTML alone does not provide strong security features. It can’t protect against various web weaknesses, like cross-site scripting (XSS) or SQL injection. These security weaknesses can lead to data hacking. Additional measures have to be taken, such as server-side scripting, to protect websites.
Server-side scripting languages like PHP, Python, or Ruby offer better security features. These languages enable developers to control data processing and apply security measures effectively.
Creating a simple webpage using pure HTML can result in many lines of code. Especially if you’re coding for complex structures. This can lead to code repetition, maintenance challenges, and increased load times for web pages.
Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) can be an alternative to streamlined code by separating the presentation from the structure. Additionally, website developers and content management systems (CMS) like WordPress simplify web development and require less manual coding.
Check out this video:
HTML stands out as the best choice for web development, but it still differs from other markup languages. Let’s explore some of these differences:
XML resembles HTML but offers more flexibility. It’s often used for data storage and exchange, allowing you to create custom tags and structures. Unlike HTML, XML isn’t concerned with how data looks.
Markdown is simpler and easier. It is commonly used for creating formatted text documents. Many people love using it for making clear documents and blog posts.
These are specialized markup languages for typesetting, especially when it comes to documents with complex math equations and symbols. Academics and scientists rely on them for accuracy in document layouts.
Each of these markup languages has its own specialty. HTML reigns supreme for web development, but XML is the choice for data. Markdown keeps things simple and is great for writers. TeX and LaTeX cater to the academic and scientific communities.
The key is to pick the right one based on what the requirements are. In some cases, trying out other markup languages can be very helpful when you need custom options, simplicity, or specific features.
If you are planning to hire an HTML developer for your website, then here are the skills to look for:
Are you a web developer looking for a job? Explore Ellow, a platform that helps you easily connect with a worldwide network of opportunities.
Recommended Read: 15 Best Front-End Technologies To Use In 2023
In conclusion, our exploration of the advantages and disadvantages of HTML reveals its main role in web development. HTML has broad browser compatibility, is cost-efficient, is easy to learn, and has flexibility, speed, and data storage capabilities through technologies like XML.
However, HTML does have disadvantages. It is static, so creating a dynamic web application is difficult. Its structural complexity can become a problem in large projects. HTML doesn’t have strong security features, and creating complex web pages can result in lengthy code.
When to use HTML and when to consider alternatives is very important.
So understanding HTML’s advantages and disadvantages is important.
Sign up with ellow, access 25,000+ pre-vetted developer profiles, and start building your development team in 48 hours.
The advantages are broad browser compatibility, cost-efficiency, and how simple and easy to learn.
HTML is not perfect for dynamic web applications, because it lacks native interactivity and dynamic behavior.
The disadvantages are its static nature, complexity, limited security features, and lengthy code.
Alternatives can be used when you need dynamic web applications, structured data storage, or increased security features.
Yes, HTML is still relevant because it remains the cornerstone of web development.



Great ideas need great people. Partner with us to bring your vision to life, or take the first step in your career by joining our team of innovators.
Looking to build your career in development? team@ellow.io