
Let’s build the future together.
Great ideas need great people. Partner with us to bring your vision to life, or take the first step in your career by joining our team of innovators.

Ever wondered how you can feel the vibration on your smartphone when you get a call or text?
Or why you feel a certain pressure when you’re playing a video game?
Well, that’s all thanks to haptic feedback.
Haptic feedback, also known as tactile (sense of touch) feedback has been around for a while, but it is only recently that it has become more mainstream among users and companies.
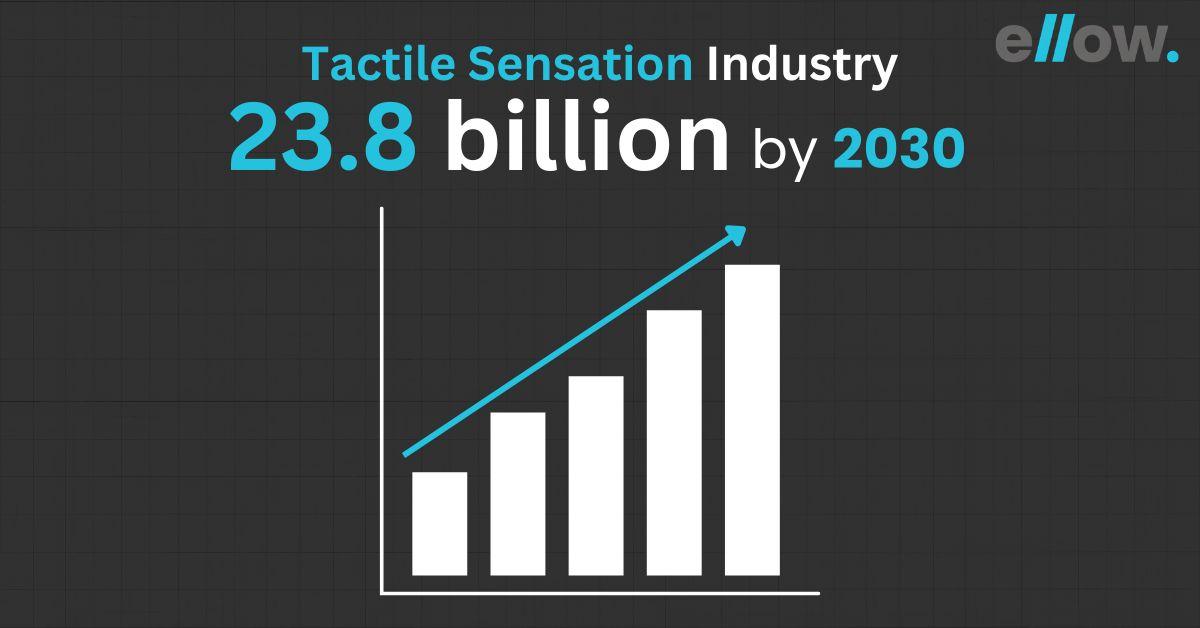
According to Precedence Research, The global haptic technology market size was valued at USD 9.2 billion in 2021 and is projected to reach around USD 23.8 billion by 2030.
One of the main reasons for the rise of haptic feedback is its ability to enhance the user experience. Whether it’s in gaming, virtual reality, or even in everyday devices like Apple iPhone, haptic feedback has the power to make users feel more engaged and immersed in the content they are interacting with.
Let’s explore more about Haptic feedback and how it works.
Haptics, in simple terms, is a technology that allows you to feel and touch virtual objects in a way that feels real like you are actually touching the object.
Just as you can see a picture on a screen or hear sounds from a speaker, haptics lets you experience physical sensations through electronic devices.
To help you understand, let’s take an example. Imagine reading a book. When you touch the book, your fingers send signals to your brain about how the book feels – the roughness or smoothness of the cover and the thickness of the pages. That’s touch sensation, and it’s part of our haptic sense.
Now, haptic technology tries to mimic these kinds of touch sensations in digital devices. For instance, when you’re using a smartphone and you press a button on the screen, you may feel a tiny vibration. That’s haptics at work. It makes your brain think that you’ve pressed a real, physical button, even though it’s just a flat glass screen.
Haptic feedback is a part of haptic technology. It’s the response that a user gets after performing an action on a haptic device. It tells your brain, “Hey, you’ve just pressed a button!”
Let’s delve deeper into Haptic feedback.
What, exactly, is haptic feedback? what is haptic feedback? Let me explain it to you in simple words.
Haptic feedback is a technology that refers to the tactile sensation or “touch” feedback a user receives when interacting with a device, such as a smartphone or gaming controller, by recreating the sense of touch through applying forces, vibrations, or motions to the user.
This feedback can take many different forms, including vibrations, pulses, or even a simple tap on your wrist.
For example, in gaming, haptic feedback can be used to simulate the sensation of gunfire, explosions, or even footsteps. This increases the realism and immersion of the gaming experience, allowing gamers to feel more connected to the game environment.

Similarly, in virtual reality, haptic feedback can be used to create the sensation of physical touch, making users feel as if they are actually touching the virtual object.
But it’s not just in gaming and virtual reality where haptic feedback is making an impact. It’s even becoming increasingly popular in everyday devices such as smartphones.
Many smartphones now use haptic feedback to create a more intuitive typing experience, making it easier and more enjoyable for users to type on their devices.
In addition, haptic feedback is being used in wearable technology like fitness trackers and smartwatches. By using haptic feedback, these devices provide users with alerts and notifications without making an audible sound.
Haptic feedback technology, at its core, uses tiny motors or actuators that vibrate or move in response to specific commands.
These vibrations are responsible for the tactile sensations that users experience when interacting with a device.
When you receive notification on your smartphone, for example, a little motor inside the device vibrates, providing you with the haptic feedback that you feel.
But haptic feedback isn’t just about vibrations; with more advanced actuators, it can also provide more complex sensations.
Some devices use piezoelectric actuators, which can create more precise vibrations, while others use linear resonant actuators (LRAs) that can produce a wider range of sensations, including pulses, taps, and even clicks.
Depending on the device and application, haptic feedback can be implemented differently.
For example, a Playstation Dual sense gaming controller uses haptic feedback to simulate the recoil of a weapon or the feeling of driving over rough terrain, while a Apple smartwatch may use haptic feedback to provide notifications without the need for an audible alert.
It’s clear that haptic feedback technology is here to stay and is likely to enhance the way we interact with digital devices and applications in the future.

When it comes to haptic feedback, software plays a huge role in controlling the device’s haptic experience. From enhancing the realism of virtual environments to creating more immersive gaming experiences, software can have a significant impact on how haptic feedback is perceived.
With the advancement of software, haptic feedback is becoming more immersive, allowing for more realistic touch sensations.

For example, in the world of VR (Virtual Reality), software can be used to create haptic feedback that simulates the sensation of touching a physical object. By manipulating the vibration patterns, software can mimic the texture and weight of objects, making the experience more realistic.
With the right programming, software can create more immersive and realistic experiences.
Force control is a type of haptic technology that simulates touch sensations by using motors or other mechanical devices. This technology is utilised in a variety of applications, ranging from robotics to gaming.
This technology can be used in devices like surgical robots to enable precise control over the force and pressure used during surgery. Surgeons, for example, can employ force control to carry out delicate procedures more accurately and precisely.
Vibrotactile feedback is a type of haptic technology that uses vibrations to mimic physical sensations. Vibrotactile feedback is used in devices such as the PlayStation DualSense controller.
This technology allows gamers to feel physical sensations that correspond to in-game events. For example, when playing a racing game, the controller may vibrate to simulate the feeling of driving over a bumpy surface.
Electrotactile feedback is another type of haptic technology that uses electrical signals to activate the nerve endings in our body. This technology is commonly used in medical devices, such as prosthetic limbs, to provide users with a sense of touch.
For example, the DARPA-developed “Luke” arm uses electrotactile feedback to provide users with a feeling of touch and feel.
Ultrasonic Mid-Air feedback is a relatively recent haptic technology that creates sensations of touch in mid-air using ultrasonic waves. This technology is employed in a variety of applications, ranging from virtual reality to telepresence.
For example, the “Ultrahaptics” device uses ultrasonic waves to create the sensation of touching a virtual object in VR and AR.
Thermal feedback is a type of haptic technology that simulates touch sensations by using heat or cold. This technology is employed in a variety of applications, ranging from games to medical devices.
For example, the “Taclim” shoes use thermal feedback to simulate the sensation of walking on different surfaces, such as snow or sand.
Microfluidics is a type of haptic technology that manipulates fluids using small channels, resulting in the creation of physical sensations. This technology is being used in various applications, from medical devices to gaming.
For example, the “Tactile Gaming Vest” uses microfluidics to create the sensation of being shot in a video game.
Surface haptics utilize vibrations to emulate tactile sensations on a flat surface, and are commonly used in touchscreens to replicate physical buttons and controls.
For example, Microsoft’s Surface tablet uses surface haptics to create the feeling of typing on a physical keyboard, even though the keyboard is actually a touchscreen.
Haptic feedback is important for many reasons. It provides a more engaging, immersive, and intuitive experience when interacting with electronic devices. It can also help to make certain tasks easier and more efficient.

Let’s talk about various aspects where Haptic feedback enhances user experiences:
Enhanced Immersion and Realism: In gaming and virtual reality, haptic feedback significantly enhances immersion. It provides tactile sensations that correspond with on-screen actions or virtual environments, making experiences feel more real and engaging.
Intuitive User Interactions: Haptic feedback in devices like smartphones and wearables (e.g., smartwatches) makes interactions more intuitive. It offers tactile responses to actions such as typing or notifications, enabling users to receive feedback without visual confirmation.
Accessibility for Disabled Users: For people with visual impairments or other disabilities, haptic feedback can be a crucial tool. It allows these users to receive information and interact with technology through touch, making devices more accessible and inclusive.
Applications in Medical and Professional Training: In medical fields, haptic feedback in training simulations provides realistic experiences. This is invaluable for training professionals in complex tasks in a safe, controlled environment.
To help you understand more, let’s look at some examples:
Mobile phones: When you type on your phone, you feel a small vibration or “buzz” with every tap. This is haptic feedback. It tells you that your action – tapping the key – has been registered by the phone. It helps you type more confidently and accurately, even without looking at the screen.
Video games: When you’re playing a video game and your controller vibrates as your character experiences something – like an explosion or a crash – that’s haptic feedback. It enhances the gaming experience by making it more immersive. You’re not just watching the action on the screen; you’re feeling it, too.
Navigation: Some smartwatches and phones give haptic feedback to guide you to your destination. For instance, your device might vibrate differently to indicate when to turn right or left. This can be helpful when you’re walking in a busy city and it’s difficult to look at your screen constantly.
Accessibility: Haptic feedback can also be essential for people with visual impairments. The vibration or other haptic signals can provide useful information to help them interact with their devices.
Training simulations: In certain professional fields like medicine or aviation, haptic feedback in virtual reality training can provide realistic experiences, helping trainees to learn and practice complex tasks in a safe, controlled environment.
The addition of haptic feedback to devices can significantly enhance the user experience by enhancing immersion and engagement.
For example, think about playing a mobile game without any haptic feedback. You might press a button on the screen, but no physical sensation would follow the action.
However, if the game had haptic feedback, you would feel a little vibration in your hand each time you touched a button, making the experience more satisfying and realistic.
But it’s not just gaming that can benefit from haptic feedback.
In fact, haptic feedback can be useful in a wide range of applications, from navigation systems that use vibrations to signal which direction to turn to medical equipment that employs haptic feedback to provide surgeons with a greater sense of touch during minimally invasive surgery.
Finally, haptic feedback is essential for improving the user experience and providing practical benefits in a variety of applications.
So, if you’re a developer or designer, think about incorporating haptic feedback into your products to elevate your product’s user experience.

The future of haptic feedback is full of potential. With advances in technology, we’re moving towards more sophisticated forms of haptic feedback.
Think about virtual and augmented reality – where the goal is to create a fully immersive experience. Haptic technology will play a pivotal role in making these experiences feel more real.
Imagine a virtual reality system that not only allows you to see and hear a virtual world but also touch and feel it. You could experience the texture of virtual objects, the impact of virtual environments, and even the sensation of virtual weather.
Haptic feedback is a growing trend in app development, and for good reason. By adding physical feedback to your app’s user interface, you can create a more intuitive and engaging experience for your users.
Now lets talk about some popular example of Apps that use Haptic feedback.
So, the next time you feel that vibration or movement from your device, remember: That’s haptic feedback at work, enhancing your experience and making technology feel a little more human.
Opting for haptic feedback in your app can be a smart choice, but do you possess the right team of developers to turn it into a reality?
This is where Ellow can come to the rescue, helping you recruit talented developers using our four-stage Human + AI vetting process. Ellow ensure to provide businesses with the top 3% of global talent in less than 48 hours.
If you want to build a team of highly qualified game developers, Ellow is the right place to begin.
Haptic feedback is a technology that uses touch sensations, such as vibrations or movements, to communicate with users. It provides tactile responses to interactions with digital devices, creating a more immersive and realistic experience.
Examples of haptic devices include video game controllers, smartphones, and certain wearable devices like smartwatches that provide vibrations or other physical responses to user input.
In iPhone devices, haptic feedback is used to enhance the user experience by providing physical responses to touch interactions. For instance, when a user selects an option or presses a button, the device will vibrate or ‘buzz’ slightly to confirm the action.
For the PlayStation 5, haptic feedback is implemented in the controller to improve gaming immersion. It provides varied tactile sensations that can simulate various textures and forces, giving players a sense of the physical interactions happening within the game.
Yes, haptic feedback can be beneficial for phone users by providing tactile confirmation of touch screen interactions, which can enhance the user experience and provide a more engaging interface.
The two types of haptics are tactile feedback and force feedback. Tactile feedback relates to touch and textures, while force feedback relates to the perception of weight and resistance.
While the concept of haptic technology has been present in various forms for centuries, the modern concept of haptic feedback in electronics can be attributed to several individuals and developments over time. One early pioneer was A. Michael Noll, who developed a man-machine tactile communication system at Bell Telephone Laboratories in the early 1970s. His work formed a significant part of the foundation for modern haptic feedback systems
The principle of haptic devices is to provide sensory feedback (usually related to touch or motion) in response to user interactions, creating a more engaging and immersive user experience.
Haptic feedback improves the user experience by providing tactile responses to digital interactions, making them feel more real and immersive. It also helps users to navigate interfaces intuitively and confirms successful actions without requiring visual attention.
In mobile devices, haptic feedback is the use of vibrations or movements to signal interactions with the device’s touchscreen interface. It can provide tactile confirmation of things like button presses or selection of items.
A haptic feedback keyboard provides physical responses, typically vibrations, when keys are pressed. This can be found on virtual keyboards on touchscreen devices, such as smartphones and tablets, and it can make typing feel more tactile and responsive.
Great ideas need great people. Partner with us to bring your vision to life, or take the first step in your career by joining our team of innovators.
Looking to build your career in development? team@ellow.io