Let’s build the future together.
Great ideas need great people. Partner with us to bring your vision to life, or take the first step in your career by joining our team of innovators.
Spring and Spring Boot are two widely used frameworks in the Java ecosystem, each offering special advantages for developers. While Spring has long been recognized as a lightweight and powerful framework for web application development, its widespread adoption has brought about challenges in terms of configuration complexity. Recognizing this, the Spring Boot framework emerged as a solution to streamline and simplify the development process.
In this article, we are going to look into a comparison between Java Spring and Spring Boot, shedding light on their key differences. We will explore the scenarios where one framework excels over the other, helping developers make informed decisions when embarking on new projects.
Whether you are a seasoned developer or just starting with Java web development, understanding the nuances between Spring and Spring Boot is crucial for informed decision-making.
According to Statista, “Spring” and “Spring Boot” were among the most favored skills in the Java tech stack worldwide, with “Spring” being preferred by 30.42% of the respondents and “Spring Boot” being chosen by 17.28%, indicating their significant role in the ecosystem.
Spring, originally introduced in 2002, is a powerful framework for developing enterprise-level web applications. Built on Java, Kotlin, and Groovy, it aims to simplify software development on the Java EE stack.
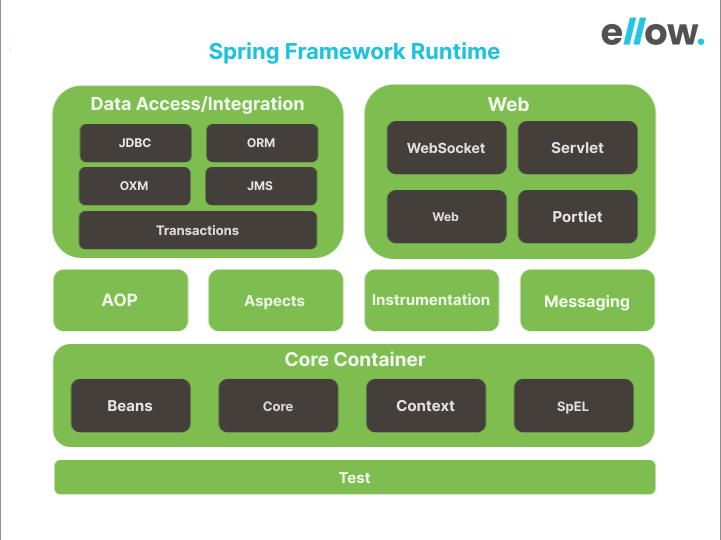
Unlike Java EE, Spring provides infrastructural support at the application level, allowing developers to focus on building business logic without worrying about specific deployment environments.
The current version, Spring 5.3.23, released on September 15, 2022, continues to be a popular choice in the software development landscape.
One of the areas where Spring Framework truly shines is in creating enterprise-grade, scalable web applications, particularly those requiring complex backend logic, data handling, and integration with various systems.
Spring is relevant for:
Spring Boot is an extension of the popular Spring framework designed to simplify and accelerate the development of Java-based applications.
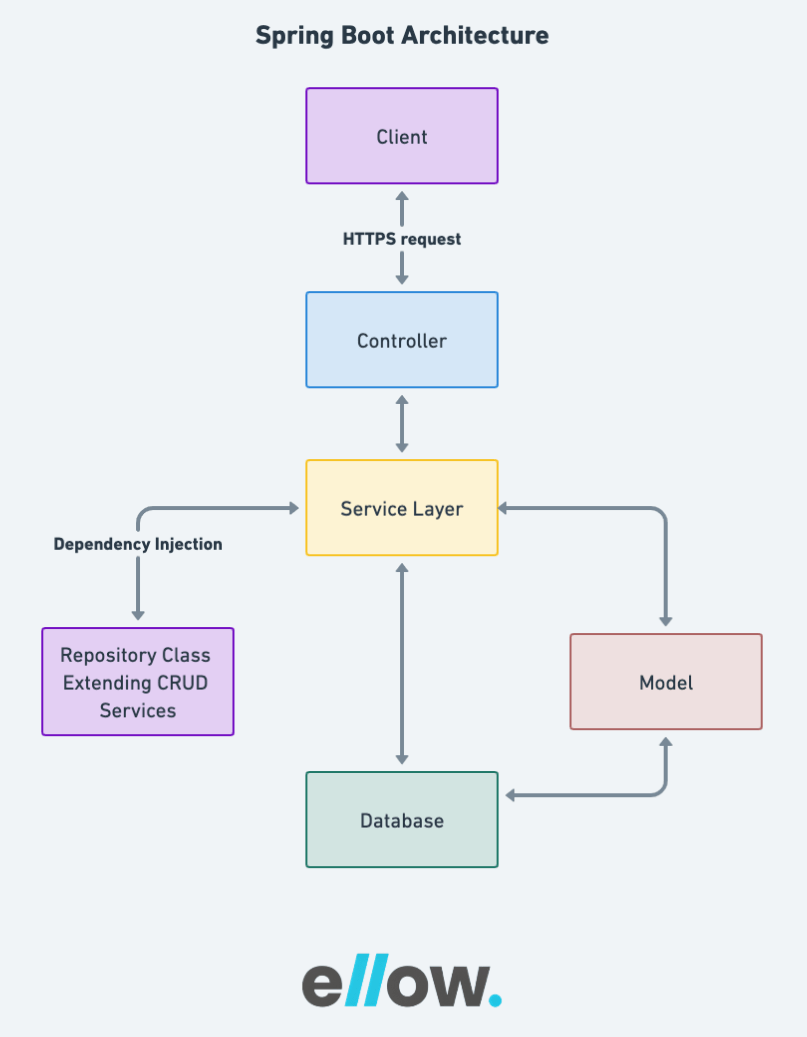
Unlike a tool for automatic code generation, Spring Boot acts as a plugin, enhancing project build automation systems. Its inception dates back to April 2014. Spring Boot offers a powerful solution for streamlining Spring-based application development, particularly in the context of microservices and smaller-scale projects.
However, developers should carefully consider their strengths and limitations based on the specific requirements of their applications.
When creating a Spring project, developers typically face time-consuming tasks such as importing modules, configuring third-party libraries, setting up data access objects (DAO), and more. Spring Boot streamlines this process with three key features:
When it comes to project configuration, Spring and Spring Boot take different approaches. Spring’s configuration can be intricate, demanding a considerable amount of code to set up. Spring Boot streamlines this process, condensing complex configurations into just a few lines. This simplicity in Spring Boot enhances development efficiency and reduces the learning curve.
In terms of control mechanisms, both Spring and Spring Boot adopt the loosely coupled inversion of control principle. In Spring, developers have more direct control over project flow, while Spring Boot handles project management internally. This distinction means that Spring Boot, by design, manages the project, offering a more guided development experience.
For security, both frameworks incorporate Spring Security, but Spring Boot simplifies dependency management. While Spring provides a comprehensive set of features for enterprise-level security, Spring Boot makes it easier to handle security-related dependencies by including them in the build configuration. This enhancement streamlines the development of secure applications in Spring Boot.
In scalability, Spring and Spring Boot have divergent recommendations. Spring, along with JEE, excels in building large-scale enterprise projects. On the other hand, Spring Boot is optimal for creating microservices deployed in Docker containers but is less suitable for extensive and monolithic software solutions. The choice between the two depends on the scale and nature of the project.
| Parameters | Spring | Spring Boot |
| Where is it used? | Spring is a Java EE framework used to develop applications | The framework, Spring Boot, is mainly used for developing REST APIs, batch processing, web applications, and more |
| Key Feature | Dependency injection is the framework’s primary or most important feature. Dependency Injection (DI) is a design technique that eliminates dependencies from computer code, making it easier to maintain and test the application. | Autoconfiguration is the primary feature of Spring Boot. By removing the need to define some beans that are part of the auto-configuration classes, autoconfiguration can help to speed up and simplify development. |
| Why it’s used | It intends to make Java Enterprise Edition development simpler and more productive for developers. | Spring Boot adds the RAD (Rapid Application Development) function to the Spring framework, allowing for faster development. |
| Application Development | The Spring framework aids in developing a loosely coupled application. | Spring Boot helps with the development of standalone applications. |
| Deployment descriptor | A deployment descriptor is necessary to run a Spring application. | Spring Boot requires no deployment descriptor. |
| Servers dependency | To test the Spring Project, we must explicitly configure the servers in the Spring framework. | Spring Boot includes pre-installed or embedded servers such as Tomcat and Jetty. |
| In-memory database support | The Spring framework does not support in-memory databases. | Spring Boot includes support for in-memory databases like H2. |
| Lines of code | Even for simple tasks, the Spring framework requires far too many lines of code (boilerplate code). | You save time and increase productivity by avoiding boilerplate code with Spring Boot. |
| Configurations | You must manually build configurations in the spring framework. | The default configurations of Spring Boot allow for faster bootstrapping. |
| Dependencies | To build a web app, Spring framework requires several dependencies. | Spring Boot can get the application up and running with just one dependency. Several more dependencies are required during build time and are automatically included in the final archive. |
| HTTP Authentication | HTTP Basic Authentication is used to enable security confirmations in Spring, requiring several dependencies and configurations. | Spring Boot also requires security dependencies but simplifies it by using the dependency spring-boot-starter-secpurity, which automatically adds all applicable dependencies to the classpath |
| XML Configuration | Spring framework requires XML configuration. | In Spring Boot, there is no need for XML configuration. |
| CLI Tools | The Spring framework does not include a command-line interface (CLI) tool for developing and testing applications. | Spring Boot includes a command-line interface (CLI) tool for developing and testing applications. |
| Testing | Due to a large amount of source code, testing is more difficult in Spring than in Spring Boot. | Testing is easier in Spring Boot due to less boilerplate code |
| Plugins | Spring framework, unlike Spring Boot, does not include a plugin for Maven, Gradle, and other build tools. | Spring Boot includes Maven and Gradle build tool plugins, providing features such as packaging executable jars. |
Our exploration of various frameworks has provided valuable insights into making informed decisions for your project. Whether opting for the comprehensive capabilities of Spring or the streamlined development process offered by Spring Boot, the key lies in aligning your project requirements with the strengths of each framework.
For web applications featuring serverless, microservice-based, or event-driven architectures, as well as those with stringent security needs and asynchronous code, Spring emerges as the optimal choice. On the other hand, Spring Boot proves its prowess in stand-alone application development and the creation of production-ready Spring applications.
The decision between Spring and Spring Boot should not be driven by a general preference for one over the other but rather by careful consideration of your project-specific needs. By doing so, you can leverage the strengths of each framework to maximize the success of your development endeavors.
Spring is a comprehensive framework suitable for enterprise-level web applications, while Spring Boot is designed for streamlined development, particularly in stand-alone applications and the creation of production-ready Spring apps.
Opt for Spring if your project involves enterprise-level web apps with serverless, microservice-based, or event-driven architecture, as well as those with high-security requirements and asynchronous code.
Spring Boot is ideal for stand-alone application development and building production-ready Spring applications, offering a quicker and more straightforward development process.
While both frameworks are part of the larger Spring ecosystem, they serve different purposes. However, they can be used together to leverage the strengths of each, depending on the specific needs of your project.
A clear understanding of the distinctions between Spring and Spring Boot empowers you to align your project requirements with the strengths of each framework, making informed decisions that contribute to the success of your digital product.

GCC vs Outsourcing vs Remote Teams: What Works in 2026

Vibe Coding vs AI Assisted Coding: The Difference That Will Define the Next Generation…

From Code Generation to Bug Detection: 10 AI Tools Every Developer Should Know in…
Please feel free to share your thoughts and we can discuss it over a cup of tea.
Get a quote
GCC vs Outsourcing vs Remote Teams: What Works in 2026

Six Things to Consider When Hiring Remote Talent

ellow.io enters remote hires market with AI-based screening process