Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a big part of our lives, affecting everything from factories that run themselves to smartwatches. AI is everywhere, helping big and small companies make their customers happier and sell more.
AI is changing big companies a lot, so it’s important to understand how it works. Have you ever thought about what makes AI work or how it makes robots and self-driving cars possible?
This article talks about the basic parts of AI. It explains how AI works and answers common questions. The article helps us understand the main things that drive the AI market, which was worth $164.99 billion in 2023.
What is AI?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the capability of machines or computers to exhibit human-like intelligence. This involves a range of technologies that empower machines to perceive, reason, act, and learn similarly to humans.
AI systems are designed to recognize and interpret their environment, make decisions, tackle complex challenges, learn from past data, and mimic behavioral patterns. These abilities enable them to perform tasks such as autonomously driving cars or using facial recognition for device security.
The AI world involves a mix of technologies including machine learning, natural language processing, and computer vision. These sophisticated technologies enable computers to process and understand human language, learn from examples, and make informed predictions.
While each technology within AI is advancing independently, its collective application alongside other technologies, data, analytics, and automation, has the potential to transform business operations. From enhancing supply chain efficiency to elevating customer service experiences, AI offers transformative solutions for businesses to achieve their objectives more effectively.
How does AI work?
AI systems start by taking in information, such as speech, text, or images. Once the data is received, the system uses rules and algorithms to process it. This involves interpreting the information, making predictions, and taking actions based on the input.
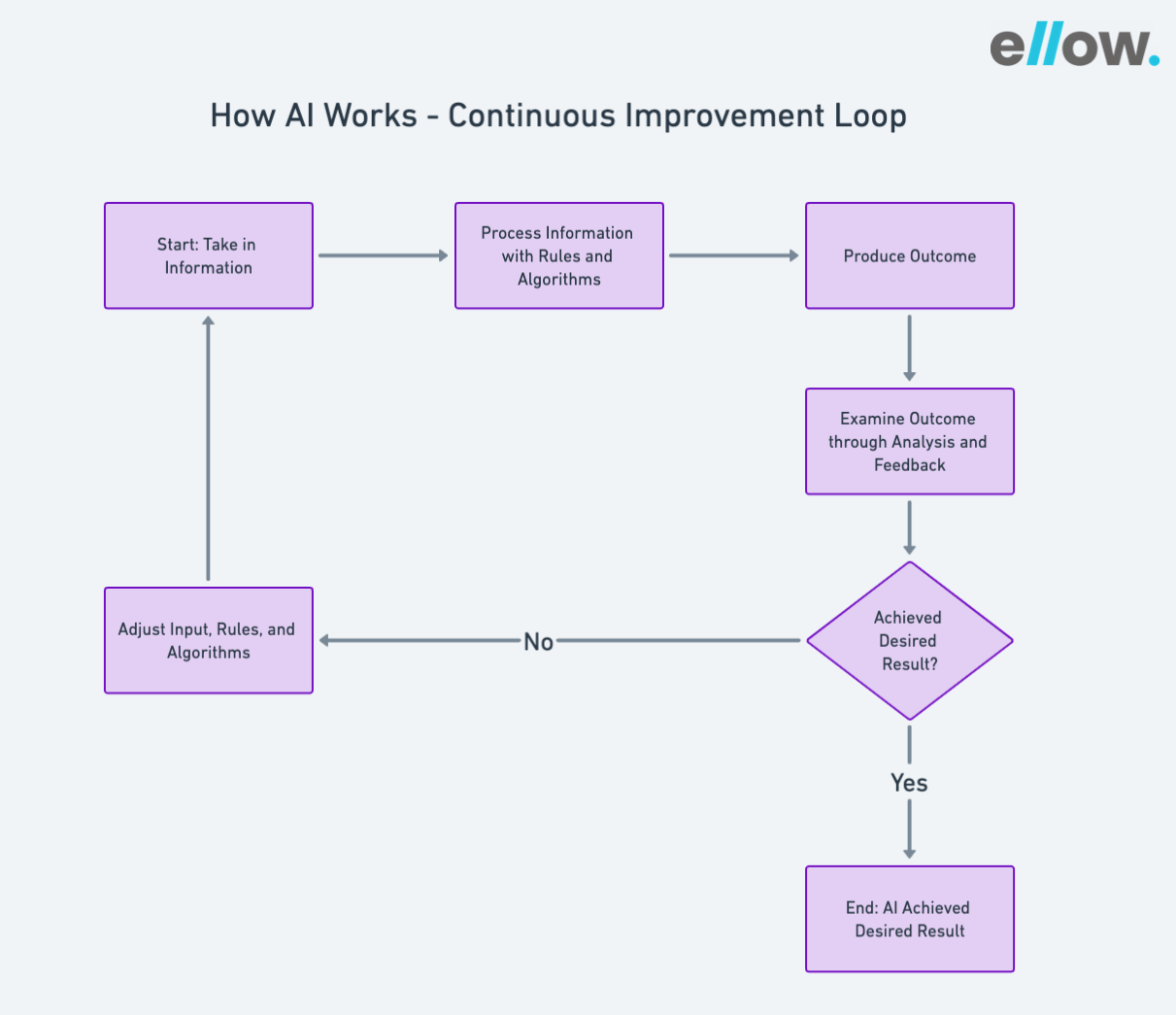
After processing, the AI system produces an outcome, which could be a success or failure in handling the input data. This result is then carefully examined through analysis, discovery, and feedback to understand how well the AI performed.
Using these assessments, the AI system makes adjustments to its input data, rules, and algorithms. This iterative process continues until the AI achieves the desired result.
In essence, AI works through a continuous loop of taking in data, processing it, evaluating the outcome, and refining its approach to improve over time.
Why is artificial intelligence important?
Artificial intelligence (AI) holds significant importance due to its transformative impact on various aspects of our lives. It has revolutionized how we work, live, and engage in activities.
Businesses are increasingly relying on AI to streamline operations and enhance efficiency. This technology has proven effective in automating tasks traditionally performed by humans, such as customer service, fraud detection, and quality control.
In many cases, AI surpasses human capabilities, especially in tasks that require precision and attention to detail. For instance, analyzing vast amounts of legal documents for accurate information is accomplished swiftly and with minimal errors by AI tools.
The ability of AI to process massive datasets provides valuable insights into business operations, uncovering aspects that might have gone unnoticed.
The growth of generative AI tools is particularly noteworthy, impacting diverse fields like education, marketing, and product design. These tools contribute to advancements by offering innovative solutions and expanding possibilities in various industries.
Prominent companies, including Alphabet, Apple, Microsoft, and Meta, recognize the crucial role of AI in maintaining competitiveness and improving operations.
Google, an Alphabet subsidiary, integrates AI into its core functions, such as the search engine, self-driving cars through Waymo, and groundbreaking advancements in natural language processing, like the transformer neural network architecture developed by Google Brain.
Components of AI
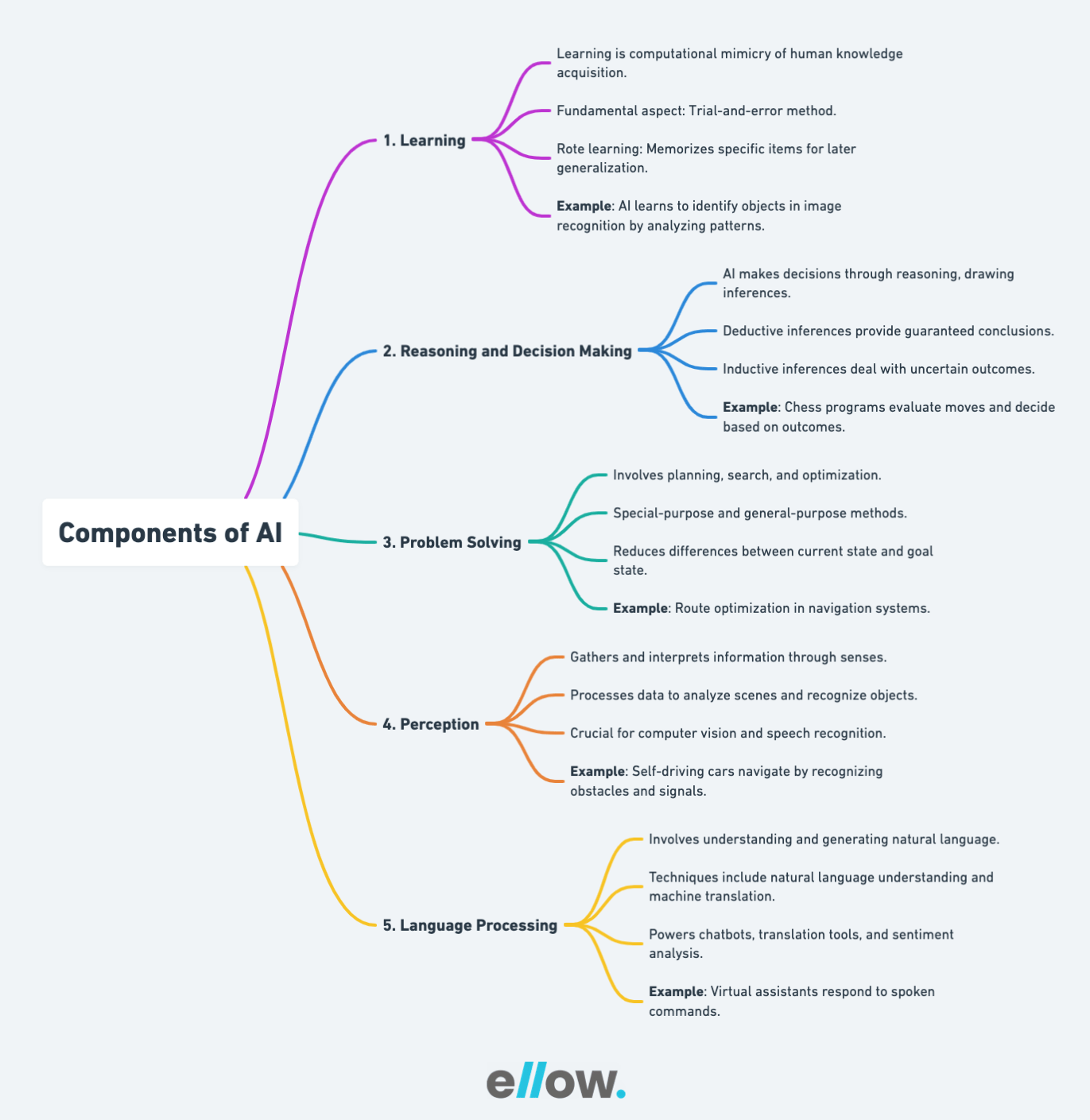
1. Learning
Learning in the context of AI is similar to how humans acquire knowledge but implemented computationally. One fundamental aspect of AI learning is the trial-and-error method. The AI system attempts various solutions to a problem and retains successful strategies in its database for future use.
Another form of learning is rote learning, where the AI memorizes specific items, such as problem-solving approaches, vocabulary, or foreign languages. This information is later generalized and applied in diverse contexts.
Example: In image recognition, AI learns to identify objects by analyzing and memorizing patterns in a vast dataset.
2. Reasoning and Decision Making
AI analyzes information and makes decisions through reasoning. This involves drawing inferences from given situations, categorized as inductive or deductive. Deductive inferences involve providing guaranteed conclusions, while inductive inferences deal with situations where outcomes are not certain.
Example: Chess-playing programs use reasoning to evaluate possible moves and make decisions based on the likely outcomes.
3. Problem Solving
AI’s problem-solving ability involves techniques like planning, search, and optimization. Special-purpose methods tailor solutions to specific features of a given problem, while general-purpose methods address a wide range of diverse issues. Problem-solving in AI includes step-by-step reduction of differences between the current state and the goal state.
Example: Route optimization algorithms in navigation systems solve the problem of finding the most efficient path between two points.
4. Perception
AI perceives its environment by gathering and interpreting information through sense organs, whether artificial or real. The system internally processes this data to analyze scenes, recognize objects, and understand their relationships and features. Perception is crucial for tasks like computer vision and speech recognition.
Example: Self-driving cars use perception to navigate roads by recognizing obstacles, pedestrians, and traffic signals.
5. Language Processing
Language processing in AI involves understanding and generating natural language. Techniques like natural language understanding, machine translation, and text generation enable AI to interact with language effectively. This allows applications like chatbots, language translation tools, and sentiment analysis to function seamlessly.
Example: Virtual assistants understand and respond to spoken commands, showcasing language processing capabilities in AI.
The Five Branches of AI
Below are the five primary branches or subfields of Artificial Intelligence (AI), each contributing uniquely to the development and capabilities of intelligent systems.
- Machine Learning
Machine Learning (ML) stands as a vital subset within AI, focusing on machines’ capacity to learn autonomously from data and algorithms. ML leverages the foundational elements of AI to make decisions without explicit programming by humans, enhancing its adaptability and problem-solving capabilities.
- Deep Learning
Deep Learning (DL) operates as a subset of machine learning, utilizing artificial neural networks (ANNs) inspired by the human brain. DL excels at extracting intricate features from data, leading to superior performance compared to traditional machine learning.
It minimizes human intervention further, although it requires substantial amounts of data. Common applications include natural language processing improvements in technologies like Amazon Alexa or Google Home.
- Natural Language Processing
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is a critical aspect of AI enabling computers to comprehend spoken words and written text. NLP is pervasive in digital assistants, chatbots, virtual assistants, and spam detection. It plays a vital role in sentiment analysis, extracting emotions and attitudes related to a product or service from textual data.
- Robotics
Robotics integrates AI to create and design autonomous or semi-autonomous robots and machines. This field often incorporates other AI technologies such as NLP and ML to enhance the capabilities of robots. AI-based robots are already making significant contributions to various industries, including healthcare, retail, and manufacturing, performing tasks with precision and efficiency.
- Fuzzy Logic
Recognizing that the world is not always binary, Fuzzy Logic comes into play in AI to handle conditions that are not strictly true or false. Fuzzy Logic resolves uncertainties by employing if-then statements or rules, utilizing linguistic variables and fuzzy rules. An example is an automatic braking system, where fuzzy logic helps determine the optimal braking force based on imprecise information, contributing to the effectiveness of AI systems in real-world, less predictable scenarios.
Common AI Applications
- Smart Assistants
Smart assistants, powered by AI, have become an integral part of daily life. These virtual companions, like Siri or Google Assistant, utilize natural language processing to answer queries, set reminders, and perform tasks, simplifying user interactions with technology.
Currently, chatbots are providing dynamic and intelligent analytics by interacting with visitors through engaging conversations. Notably, more than 67% of online visitors express a preference for chatbots.
- Financial Fraud Detection
AI plays a crucial role in safeguarding financial transactions. By analyzing patterns, anomalies, and user behaviors, AI algorithms can detect and prevent fraudulent activities, ensuring the security of online banking, credit card transactions, and digital payments.
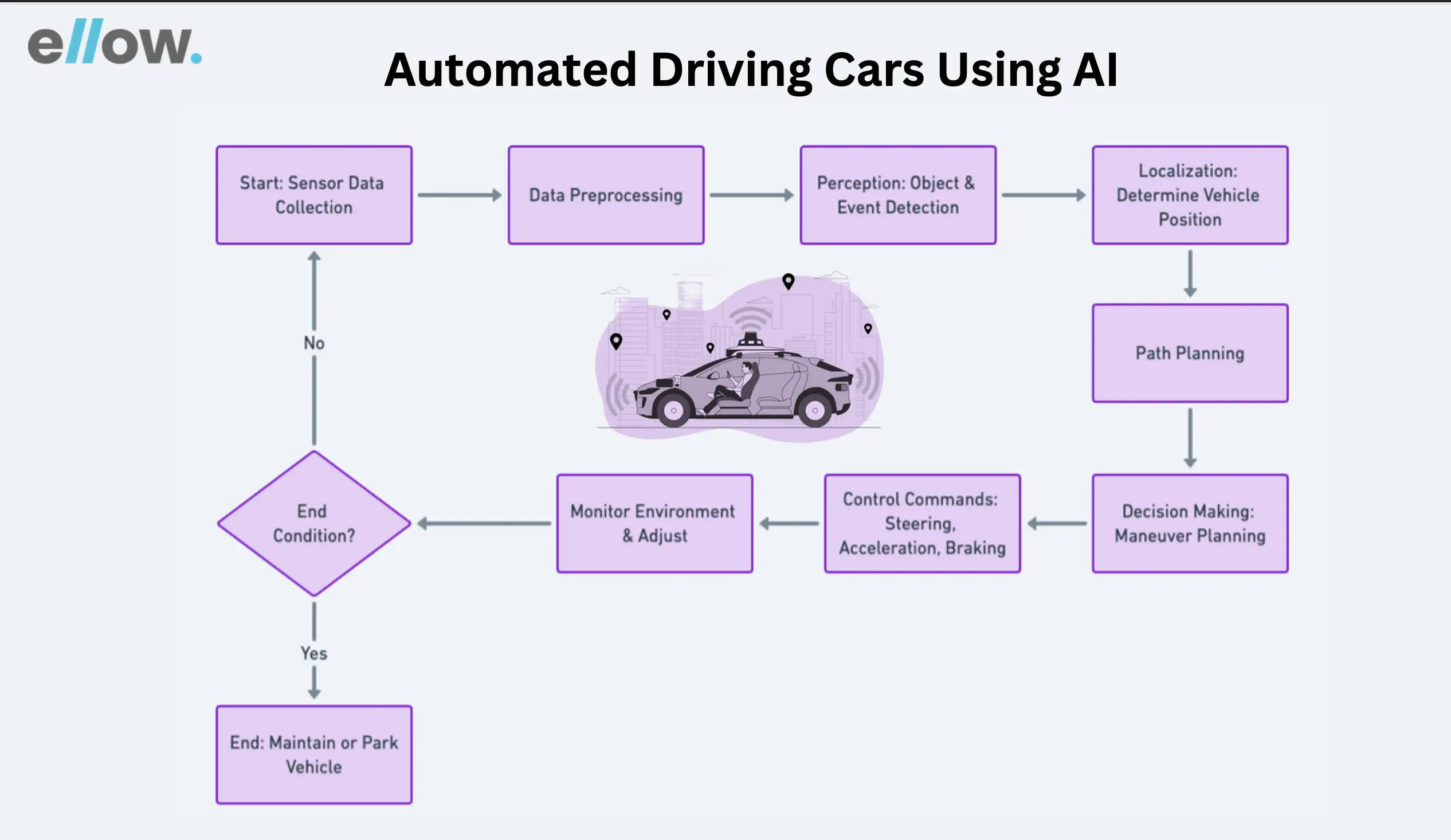
- Autonomous Vehicles
AI is steering the future of transportation with the development of autonomous vehicles. Through advanced sensors and machine learning algorithms, self-driving cars can navigate roads, make real-time decisions, and enhance overall road safety, paving the way for a revolution in the automotive industry.
- Predictive Maintenance in Manufacturing
In the manufacturing sector, AI is employed for predictive maintenance. By analyzing data from sensors and equipment, AI algorithms can predict when machinery is likely to fail, allowing businesses to schedule maintenance proactively, minimize downtime, and optimize production processes.
- Educational Technology (EdTech)
AI is transforming the education landscape through personalized learning experiences. Educational technology platforms use AI to analyze students’ progress, adapt learning materials to individual needs, and provide targeted feedback, enhancing the effectiveness of education in a digitally driven era.
Key Challenges of AI
- AI Algorithm Bias
AI systems rely on trained data, and as we delve into AI, biases within the data become apparent. These biases can include factors like race, gender, or ethnicity, affecting critical decisions like job interviews or loan approvals. To address this, companies like Microsoft and Facebook are developing anti-bias tools to identify and rectify biased perspectives in AI algorithms.
- Black Box Problem
AI algorithms often function as black boxes, making their inner workings unclear. While we can see the predictions, understanding how the algorithm reaches those predictions is challenging. Techniques like ‘local interpretable model-agnostic explanations’ (LIME) are being employed to provide additional information for each prediction, enhancing algorithm transparency and reliability.
- Requirement of High Computing Power
AI demands substantial computing power, especially for training models. The rise of deep learning algorithms necessitates additional cores and GPUs, often requiring supercomputers. Limited global availability and high costs of supercomputers hinder AI implementation in areas such as astronomy, where it could be valuable for tasks like asteroid tracking.
- Complicated AI Integration
Integrating AI into existing corporate infrastructure is more complex than typical software updates. Compatibility with current programs and ensuring AI integration doesn’t adversely affect existing processes are crucial. Establishing an efficient AI interface is necessary for the smooth management of AI infrastructure, but the transition can be challenging.
- Lack of Understanding of Implementation Strategies
Despite AI’s transformative potential, there is a lack of clear understanding regarding its implementation strategies. Businesses must identify areas benefiting from AI, set realistic goals, and establish feedback loops for continuous improvement. Corporate managers need a comprehensive understanding of AI technologies, trends, and limitations to implement AI solutions effectively.
- Legal Concerns
Organizations must navigate legal concerns related to AI, especially concerning sensitive data collection. Even if data collection is legal, its aggregation can have negative implications.
Latest trends in AI in 2024
The AI landscape in 2024 is witnessing notable trends that impact various sectors:
- Advancements in IoT Integration:
AI’s influence on the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to expand. IoT devices, which connect to the internet, are becoming more adept at collecting and sharing data, fostering a seamless integration of smart products.
- Innovations in Medical Sensory Perception:
A groundbreaking development in medicine involves the integration of artificial sensors with human senses. Technologies like corneal implants and laser tactile canes are emerging, showcasing AI’s role in enhancing sensory perception for medical applications.
In the healthcare sector, the artificial intelligence (AI) market was valued at approximately 11 billion U.S. dollars globally. Projections indicate substantial growth, with expectations that the worldwide healthcare AI market will reach nearly 188 billion U.S. dollars by 2030.
Anticipated to expand at a compound annual growth rate of 37 percent from 2022 onwards, the sector is poised for significant advancements in the next decade according to Statista.
- Evolving Educational Technologies:
AI’s prominent role in education is growing, leading to an expansion of online and virtual learning options for individuals of all ages. This trend also involves the integration of AI-powered robots in educational settings, potentially transforming teaching methodologies.
- Enhancements in Business Analytics:
Machine learning algorithms are increasingly refining Customer Relationship Management (CRM) platforms. The goal is to optimize customer service and satisfaction by leveraging AI’s capabilities for data analysis and insights. Anticipated to attain a market value of $49 billion, the most promising developments are still ahead!
- Optimizing Manufacturing Processes:
AI’s impact on manufacturing is significant, with projections suggesting substantial market growth. Current applications include improving daily operations, introducing innovative products, and providing accurate forecasts for future financial needs within the manufacturing sector.
- Productivity Boost in Legal Practices:
Attorneys are leveraging AI to enhance productivity and efficiency in legal processes. From data collection for contracts to identifying optimal strategies for specific legal situations, AI platforms are becoming invaluable tools for legal professionals.
Conclusion
Looking into the various facets of intelligence, unraveling the workings of AI, and exploring its diverse learning methods, we can affirm with certainty that AI stands poised as the harbinger of the future. It emerges as a steadfast ally in intelligent automation, making it a worthwhile pursuit to grasp the fundamentals of AI.
The impact of Artificial Intelligence extends beyond the realm of business, offering a gateway for enhancing services and building stronger connections with audiences. Beyond commercial applications, AI serves as the linchpin for automation, ranging from self-driving cars to voice-command-operated home systems.
Embracing a foundational understanding of AI is not just an investment in knowledge but a pathway to navigating the evolving landscape of innovation and efficiency.
Recommended Reads
AI Trends in Recruitment: Revolutionizing the Hiring Landscape
Generative AI vs. Predictive AI: What is the difference?
FAQs
What are the fundamental components of Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
The key components of AI include machine learning, natural language processing, and expert systems. These elements work in tandem to enable AI systems to perform various tasks intelligently.
How does machine learning contribute to the components of AI?
Machine learning is a vital component of AI, allowing systems to learn from data and improve their performance over time. It involves the use of algorithms that enable machines to make decisions or predictions without explicit programming.
What role does natural language processing play in AI?
Natural language processing (NLP) is a crucial component that empowers AI systems to understand, interpret, and generate human-like language. This capability is essential for effective communication between humans and AI.
How do expert systems enhance the functionality of AI?
Expert systems are specialized AI components designed to mimic human expertise in a particular domain. By incorporating knowledge bases and rule-based reasoning, expert systems contribute to the decision-making capabilities of AI in specific areas.
Can you provide examples of applications where these AI components are utilized?
AI components find applications in various fields. For instance, machine learning is applied in recommendation systems and image recognition, while natural language processing is utilized in virtual assistants. Expert systems are often employed in medical diagnosis and decision support systems